The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change’s (IPCC) synthesis report recently landed with an authoritative thump, giving voice to hundreds of scientists endeavouring to understand the unfolding calamity of global heating. What’s changed since the last one in 2014? Well, we’ve dumped an additional third of a trillion tonnes of CO₂ into the atmosphere, primarily from burning fossil fuels. While world leaders promised to cut global emissions, they have presided over a 5% rise.
The new report evokes a mild sense of urgency, calling on governments to mobilise finance to accelerate the uptake of green technology. But its conclusions are far removed from a direct interpretation of the IPCC’s own carbon budgets (the total amount of CO₂ scientists estimate can be put into the atmosphere for a given temperature rise).
The report claims that, to maintain a 50:50 chance of warming not exceeding 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels, CO₂ emissions must be cut to “net-zero” by the “early 2050s”. Yet, updating the IPCC’s estimate of the 1.5°C carbon budget, from 2020 to 2023, and then drawing a straight line down from today’s total emissions to the point where all carbon emissions must cease, and without exceeding this budget, gives a zero CO₂ date of 2040.
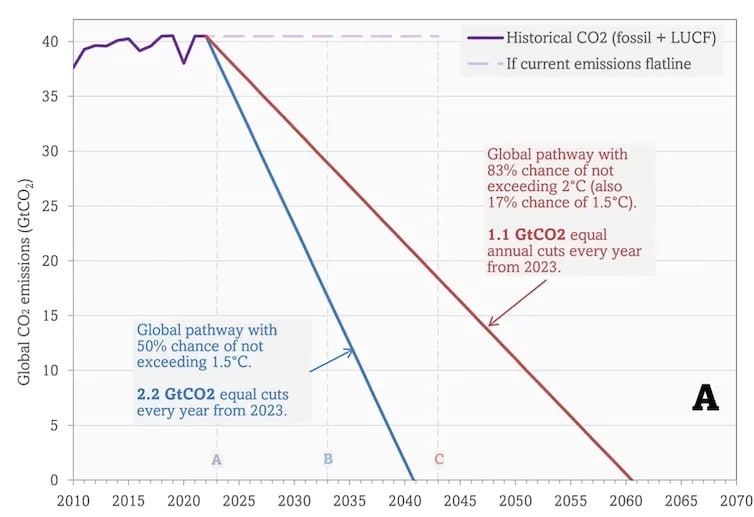
If emissions stay at their current levels, we will exhaust the 50% chance of 1.5°C in 9 years. If we begin to immediately cut emissions following the blue line, then to stay within the carbon budget for 50:50 chance of not exceeding 1.5°C we need zero global emissions by 2040. The vertical axis represents how much carbon is emitted each year – note the pandemic-related blip in 2020. (Graph: Kevin Anderson / Climate Uncensored, Author provided)
A full description of the above chart is available here.
Given it will take a few years to organise the necessary political structures and technical deployment, the date for eliminating all CO₂ emissions to remain within 1.5°C of warming comes closer still, to around the mid-2030s. This is a strikingly different level of urgency to that evoked by the IPCC’s “early 2050s”. Similar smoke and mirrors lie behind the “early 2070s” timeline the IPCC conjures for limiting global heating to 2°C.
IPCC science embeds colonial attitudes
For over two decades, the IPCC’s work on cutting emissions (what experts call “mitigation”) has been dominated by a particular group of modellers who use huge computer models to simulate what may happen to emissions under different assumptions, primarily related to price and technology. I’ve raised concerns before about how this select cadre, almost entirely based in wealthy, high-emitting nations, has undermined the necessary scale of emission reductions.
In 2023, I can no longer tiptoe around the sensibilities of those overseeing this bias. In my view, they have been as damaging to the agenda of cutting emissions as Exxon was in misleading the public about climate science. The IPCC’s mitigation report in 2022 did include a chapter on “demand, services and social aspects” as a repository for alternative voices, but these were reduced to an inaudible whisper in the latest report’s influential summary for policymakers.
The specialist modelling groups (referred to as Integrated Assessment Modelling, or IAMs) have successfully crowded out competing voices, reducing the task of mitigation to price-induced shifts in technology—some of the most important of which, like so-called “negative emissions technologies”, are barely out of the laboratory.
The IPCC offers many “scenarios” of future low-carbon energy systems and how we might get there from here. But as the work of academic Tejal Kanitkar and others has made clear, not only do these scenarios prefer speculative technology tomorrow over deeply challenging policies today (effectively a greenwashed business-as-usual), they also systematically embed colonial attitudes towards “developing nations”.

March 2023’s synthesis report capped eight years of research. (Photo: IISD/ENB/Anastasia Rodopoulou)
With few if any exceptions, they maintain current levels of inequality between developed and developing nations, with several scenarios actually increasing the levels of inequality. Granted, many IAM modellers strive to work objectively, but they do so within deeply subjective boundaries established and preserved by those leading such groups.
What happened to equity?
If we step outside the rarefied realm of IAM scenarios that leading climate scientist Johan Rockström describes as “academic gymnastics that have nothing to do with reality”, it’s clear that not exceeding 1.5°C or 2°C will require fundamental changes to most facets of modern life.
Starting now, to not exceed 1.5°C of warming requires 11% year-on-year cuts in emissions, falling to nearer 5% for 2°C. However, these global average rates ignore the core concept of equity, central to all UN climate negotiations, which gives “developing country parties” a little longer to decarbonise.
Include equity and most “developed” nations need to reach zero CO₂ emissions between 2030 and 2035, with developing nations following suit up to a decade later. Any delay will shrink these timelines still further.
Most IAM models ignore and often even exacerbate the obscene inequality in energy use and emissions, both within nations and between individuals. As the International Energy Agency recently reported, the top 10% of emitters accounted for nearly half of global CO₂ emissions from energy use in 2021, compared with 0.2% for the bottom 10%. More disturbingly, the greenhouse gas emissions of the top 1% are 1.5 times those of the bottom half of the world’s population.
So where does this leave us? In wealthier nations, any hope of arresting global heating at 1.5 or 2°C demands a technical revolution on the scale of the post-war Marshall Plan. Rather than relying on technologies such as direct air capture of CO₂ to mature in the near future, countries like the UK must rapidly deploy tried-and-tested technologies.
Retrofit housing stock, shift from mass ownership of combustion-engine cars to expanded zero-carbon public transport, electrify industries, build new homes to Passivhaus standard, roll-out a zero-carbon energy supply and, crucially, phase out fossil fuel production.
Three decades of complacency has meant technology on its own cannot now cut emissions fast enough. A second, accompanying phase, must be the rapid reduction of energy and material consumption.
Given deep inequalities, this, and deploying zero-carbon infrastructure, is only possible by re-allocating society’s productive capacity away from enabling the private luxury of a few and austerity for everyone else, and towards wider public prosperity and private sufficiency.
For most people, tackling climate change will bring multiple benefits, from affordable housing to secure employment. But for those few of us who have disproportionately benefited from the status quo, it means a profound reduction in how much energy we use and stuff we accumulate.
The question now is, will we high-consuming few make (voluntarily or by force) the fundamental changes needed for decarbonisation in a timely and organised manner? Or will we fight to maintain our privileges and let the rapidly changing climate do it, chaotically and brutally, for us?

