In a variant of the Sowing Doubt About China—But At What Cost? propaganda scheme, the New York Times makes the (somewhat racist) claim that China lacks the capability to turn talent into innovation:
What DeepSeek’s Success Says About China’s Ability to Nurture Talent (archived)—New York Times, Feb 10 2025
The subtitle reveals the core thesis:
China produces a vast number of STEM graduates, but it hasn’t been known for innovation. Cultural and political factors may help explain why.
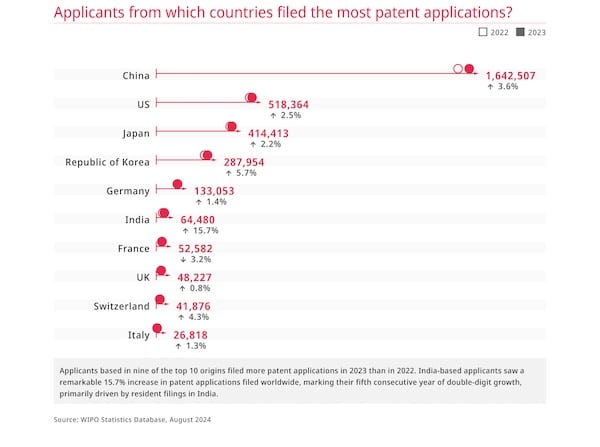
In a globalized world the innovation ability of a country can be measured by the number of global patents it files.
The World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO) provides data on these.
China, which the NYT says is not known for innovation, is by far leading the pack.
One might argue that China, with four times the population of the United States, should have innovated even more than that. But seen under this aspect the U.S. is also far from the top.
Per million inhabitants China filed 1.2 patents per year while the United States filed 1.5. But the real leaders here are South Korea with 5.5 patents per year per million people followed by Japan with 3.3/y/million.
Real world numbers are not sufficient to support the NYT‘s central thesis. That is why it barely mentions some. Its argument comes down to a political one:
Pavel Durov, the founder of the messaging platform Telegram, said last month that fierce competition in Chinese schools had fueled the country’s successes in artificial intelligence. “If the U.S. doesn’t reform its education system, it risks ceding tech leadership to China,” he wrote online.The reality is more complicated. Yes, China has invested heavily in education, especially in science and technology, which has helped nurture a significant pool of talent, key to its ambition of becoming a world leader in A.I. by 2025.
But outside of the classroom, those graduates must also contend with obstacles that include a grinding corporate culture and the political whims of the ruling Communist Party. Under its current top leader, Xi Jinping, the party has emphasized control, rather than economic growth, and has been willing to crack down on tech firms it deems too influential.
If that is indeed so why is it supposed to be bad?
Is it really healthy for a country to have Apple, Nvidia, Microsoft, Amazon and Alphabet (Google) leading in Market Cap? The author fails to follow that question.
She instead misleads about the alleged crack-down:
Beijing has blessed the A.I. sector–for now. But in 2020, after deciding that it had too little control over major companies like Alibaba, it launched a sweeping, yearslong crackdown on the Chinese tech industry.
The crack-down against Alibaba owner Jack Ma came when he tried to expand Alibaba into the so called fin-tech business.
Juggling with credit and various derivatives thereof is a part of the economy that is better to be kept under control. The 2008 mortgage credit crisis and the following government bailout of private banks have taught as much. Pouring money and talent into a sector that is not productive and carries high risk is not in any societies’ best interest.
In an aside the NYT author comes near to acknowledging that:
(DeepSeek’s founder, Liang Wenfeng, pivoted to A.I. from his previous focus on speculative trading, in part because of a separate government crackdown there.)
How can one conclude from there that China still has to liberalize?
But the best way for China to capitalize on its well-educated, ambitious A.I. work force may be for the government to get out of the way.
China’s government planning and control over education and its economy has led to its astonishing rise.
Lacking the abundance of capital which OpenAI and other U.S. companies are spending on their attempts to monopolize their fields, DeepSeek had to innovate. It did so and has beaten its competition.
How less government intervention would have led to a better performance than China has shown is difficult to argue. The NYT for one fails at it.