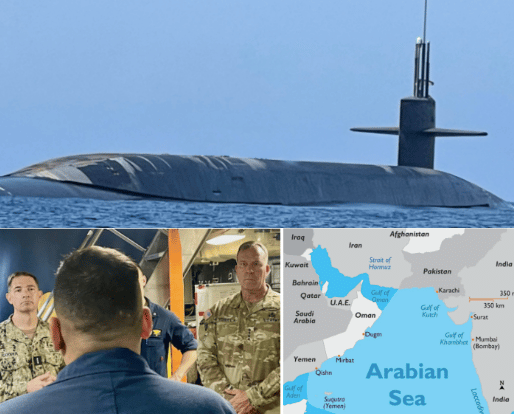
Last week on October 19 the U.S. Navy announced that “General Michael ‘Erik’ Kurilla [lead image, lower right] , commander of CENTCOM, conducted a visit aboard the USS West Virginia [top], a U.S. Navy Ohio-class nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarine at an undisclosed location at sea in international waters in the Arabian Sea. Kurilla was joined on the USS West Virginia by Vice Admiral Brad Cooper [lower left], commander of the U.S. Navy’s Fifth Fleet and NAVCENT.”
The Fifth Fleet and the Naval Forces Central Command (NAVCENT) are headquartered at Bahrain on the Persian Gulf. From Bahrain down the Gulf to the Masirah Island airbase, off Oman, is a flight distance of 1,047 kilometres. From Masirah to the West Virginia and its escort was within helicopter flight range.
Two days later, the Pentagon reported that “on October 21, Secretary of Defense Lloyd J. Austin III spoke by phone with Russian Minister of Defense Sergey Shoygu. Secretary Austin emphasized the importance of maintaining lines of communication amid the ongoing war against Ukraine.” They spoke again on October 23, according to Austin’s spokesman, because Shoigu had “requested a follow up call.”
Less than 24 hours elapsed before Austin telephoned his Kiev counterpart, Alexei Reznikov, to “reiterate[d] that the United States rejects the public and false allegations by Russia about Ukraine and any attempt to use them as a pretext for further Russian escalation of its unlawful and unjustified war against Ukraine.”
The same day, in the Moscow evening, the U.S. Joint Chiefs of Staff issued a communiqué confirming that “Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Gen. Mark A. Milley spoke with Chief of Russian General Staff Gen. Valery Gerasimov today by phone. The military leaders discussed several security-related issues of concern and agreed to keep the lines of communication open. In accordance with past practice, the specific details of their conversation will be kept private.” RIA, the Russian state news agency, reported that in their conversation the generals “discussed the possibility raised by Moscow that Ukraine might use a ‘dirty bomb’.”
The call took place shortly after a similar conversation between Gerasimov and his British counterpart.
Admiral Sir Tony Radakin, the British chief of staff, announced that Gerasimov had requested their conversation. According to Radakin, he had “rejected Russia’s allegations that Ukraine is planning actions to escalate the conflict, and he restated the UK’s enduring support for Ukraine. The military leaders both agreed on the importance of maintaining open channels of communication between the UK and Russia to manage the risk of miscalculation and to facilitate de-escalation. The conversation followed the Defence Secretary’s call with his Russian counterpart yesterday and a call between the Foreign Ministers of France, the UK, and the USA last night.”

Left to right: General Valery Gerasimov; General Mark Milley; Admiral Sir Tony Radakin; General Lloyd Austin.
That preceding call of foreign ministers, involving Secretary of State Antony Blinken for the U.S., produced a joint statement of “committ[ment] to continue supporting Ukraine’s efforts to defend its territory for as long as it takes. Earlier today, the defense ministers of each of our countries spoke to Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoygu at his request. Our countries made clear that we all reject Russia’s transparently false allegations that Ukraine is preparing to use a dirty bomb on its own territory. The world would see through any attempt to use this allegation as a pretext for escalation. We further reject any pretext for escalation by Russia.”
Blinken then telephoned his Kiev counterpart, Dmitry Kuleba, to repeat both parts of the message—that the Ukraine should not escalate to using a nuclear weapon, and that Russia should do likewise.
In case there was hardness of hearing or weakness of command and control in Kiev, or ambiguity between what Reznikov and Kuleba thought they were hearing from Washington and London, British Defence Secretary Ben Wallace had met Austin at the Pentagon on October 18. They then telephoned to talk again on Sunday, when they “reaffirm[ed] the U.S.-UK defense relationship and the importance of transatlantic cooperation. Their conversation today was a continuation of their discussion at the Pentagon last week, which covered a wide range of shared defense and security priorities, including Ukraine.”

Source: https://vz.ru/
“The U.S. has shown its readiness to launch a nuclear strike on Russia.” October 24, 2022
Text: Alexander Timokhin
Austin telephoned Kiev again yesterday to repeat to Reznikov that he should make sure the allegation of a Ukrainian nuclear weapon escalation was “false”; and that the allies had given Moscow this assurance in exchange for Moscow’s undertaking against “further escalation”—read Russian nuclear response.
At the same time yesterday, Vzglyad, the Moscow security publication, published its assessment of the escalating nuclear threat to Russia from the U.S., as the Kremlin, Defence Ministry, General Staff and the Stavka see it now. A translation into English follows.
Does the United States have the ability to instantly, within a few minutes, launch a disarming and unreciprocated nuclear strike on Russia? For decades, it was assumed that no, any U.S. attack would cause an immediate similar response from the Russian armed forces. But now there is reason to believe that Washington has come to a different conclusion—and brazenly demonstrates it.
On Thursday, October 20, an exceptional event took place in the Arabian Sea. It was publicly announced that Michael Kurilla, commander of the U.S. Central Command, paid a visit to the Ohio-class West Virginia SSBN (submarine with ballistic nuclear missiles), which specially surfaced in the Arabian Sea. This submarine, like all its ‘sister ships’, is armed with 24 Trident II ballistic missiles, each of which can carry 10 warheads at a maximum, which in total gives the vessel an ammunition supply of 240 strategic nuclear warheads.
But the fact is that the purpose of such vessels is always to be secretive and never to reveal the location of their patrol. The fact that now the location of this SSB [ballistic missile submarine] is expressly highlighted, it is impossible to understand otherwise than a special signal. It is difficult to remember when earlier in this way any American military commander so clearly and openly visited a boat at sea on combat duty. All this is directly related to the nuclear deterrence system that exists between Russia and the United States.
Nuclear deterrence and nuclear attack
Nuclear war, the preparation for it and its conduct, is not as simple as the average person thinks. Let’s briefly list the key concepts.
When two sides—in this case, Russia and the United States—both have nuclear weapons, and the means of their delivery to enemy territory, a missile attack warning system, and the technical capability to launch ballistic missiles after this system detects the launch of enemy missiles, then a simple missile attack becomes suicide for the attacker. If the United States or Russia launches their ballistic missiles at the enemy, the enemy will be able to launch their missiles before the attacking side’s missiles reach their target.
Such a strike, when a counterattack is carried out before the enemy’s missiles have reached target, is called a ‘counter-counter’ [ответно-встречным]. It is applied with the help of intercontinental ballistic missiles based in deep underground silos and ready to launch immediately.
The problem is that the interval from launch command to the counter-strike takes time. And besides, it is necessary that someone from among the leaders who have the authority to order such a strike would be physically able to do it–that is, would be alive, conscious, and so on.
This vulnerability can be exploited by delivering a so—called обезглавливающий удар (for Americans, the term is decapitation strike). A strike aimed at destroying the leadership. There are various ways to prevent or to balance the consequences of such a strike–we will not list them, nor the methods of their application (not only by missile strike).
In addition to the decapitating blow, there is such a thing as a disarming blow (удар обезоруживающий–counterforce strike). Its goal is to attack the nuclear arsenal of the victim country in such a way that the enemy, even with a workable leadership, simply does not have time to launch its missiles in response. To do this, the time for which the blow is struck should be less than the enemy needs to make a decision and pass the order to the launchers.
Therefore, in addition to providing a retaliatory nuclear strike, the country’s nuclear forces have been invested with the means of ensuring the guaranteed possibility of a retaliatory strike. Which will be produced even if the enemy struck first, and all his missiles hit their targets before at least something was launched in response. The most common way to ensure a retaliatory strike is strategic submarines. As a result, the enemy’s attack in any case causes a counter-counter or retaliatory strike. Nuclear war turns out to be a dead end; it cannot be won; and even the initiator who has attacked successfully also dies.
This principle is called “mutually assured destruction”. It was this, and not anything else, that guaranteed the absence of major wars on our planet since 1945.
However, today the situation is somewhat different. The number of nuclear warheads has become such that the exchange of nuclear strikes cannot lead to the guaranteed death of all living things. The number of carriers of nuclear weapons has fallen to such numbers that even after a massive, all-out strike, wildlife, untouched cities and towns, and people will remain in the Northern Hemisphere. A nuclear war without the death of all participants has become possible.
The second problem is the combat stability of the Russian nuclear forces in their current configuration. Russia was able to revive the Missile Attack Warning System (SPRN). The missiles that are supposed to retaliate and counter-strike are regularly updated.
But now our fleet has fewer ships than Japan. There is no possibility to intercept or block all dangerous waters with the operations of Russia’s anti-submarine forces. And this means that, as in the case of the Arabian Sea, the Americans and the British who can hold the area, will be free to manoeuvre there in order to strike from locations where the missiles can reach us too quickly. For example, in the Northern, Norwegian, Barents, Mediterranean and Arabian Seas.
Russian strategic submarines are few in number today compared to the Soviet times. Together with the qualitative superiority of the U.S. Navy, this creates an environment where the Americans can destroy our submarines immediately before the attack begins. This, alas, is a fact known to specialists. At the same time, 44% of all strategic nuclear warheads in Russia are placed on submarines. And almost all of them are in two (!) fleet bases vulnerable to the first strike. The Russian strategic aviation has never learned to fight like the American one, and it is not a means of guaranteed retaliation.
The combination of these factors creates a technical opportunity for the United States to launch a successful disarming nuclear strike against Russia without receiving a significant blow in response. At the same time, the intensity of anti-Russian propaganda is such that the western man in the street will not have to justify anything–from that perspective everything is already prepared. And right now there is the hint of the possibility of such a strike when the West Virginia surfaced in the Arabian Sea.
Chinese factor, flight time and impact mechanics
Some experts believe that the American SSB was carrying out tasks to put pressure on China during the CPC [Chinese Communist Party] Congress. On the one hand, it is indeed easy to attack China from the Arabian Sea ‘from the rear’—the approach of missiles to its populated areas will be from its deserts in the west of the country.
But there is no logic in such pressure. The Americans don’t know exactly where the Chinese have missiles. In addition, China does not have its own full-fledged SPRN [missile attack warning system]. The Americans can organize a sudden strike on this country with Pacific submarines from other directions. They simply do not need to threaten China from the Indian Ocean, and without this, they have a full array of threats.
In contrast to China, the coordinates of Russian underground launchers and the corridors along which mobile installations moved until recently are known to the Americans extremely accurately. We gave them all the information ourselves during mutual inspections of each other’s missile positions. Thus, the strategic missile submarine in the Arabian Sea is a hint not to China, but to Russia. At the very least we should not rule it out.
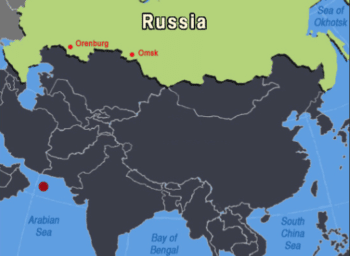 In order for the strike on our country to be successful, it must be delivered faster than we will have an alarm, an assessment of the situation for the command to launch. To do this, the distance from which the strike is carried out must be about 3,000 kilometres, otherwise the flight time of the missiles will be too long. So now let’s look at the map.
In order for the strike on our country to be successful, it must be delivered faster than we will have an alarm, an assessment of the situation for the command to launch. To do this, the distance from which the strike is carried out must be about 3,000 kilometres, otherwise the flight time of the missiles will be too long. So now let’s look at the map.
When the SSB is deployed in the northern part of the Arabian Sea, it just happens to be at about such a distance from the installations of the 31st Missile Army of the RVSN [Russian Strategic Rocket Forces, HQ Orenburg] and some parts of the 33rd Guards Army of the RVSN [Russian Strategic Rocket Forces, HQ Omsk], which allows the submarine to deliver the same disarming blow in the minimum flight time.
It is clear that such a task cannot be solved by one submarine. And it is clear that such a task cannot be solved solely from the Arabian Sea. But no one is talking about ‘one’ and ‘only’. The deployment of SSBMS in this sea area is not a preparation for a strike against Russia. But this is a demonstration that technically the United States can strike such a blow if it sees fit. And they’re not bluffing.
There is one technical aspect that is little-known to the layman. A ballistic missile can fly not only along the normal trajectory for itself, when the payload is lifted into the upper point of the trajectory and drops down from there. In addition to ballistic trajectories, missiles can also fly along the so-called flat (depressed in English terminology). The meaning of the flat trajectory is that the rocket goes very low, not even rising to 300 kilometres. With such a trajectory, ranges and accuracy suffer greatly, the dispersion of combat warheads increases, but this turns out to give a serious gain in flight speed to the target and a very small flight time.
If during a strike from the Arabian Sea, for example on the 13th missile division [13th Orenburg Red Banner Rocket Division] in the Orenburg region, employing a conventional trajectory, the flight time of the missiles is comparable to the time required for making a decision and passing the command for a counter-strike. However, when striking from there by a flat trajectory, the picture changes dramatically, and not in our favour.
At the same time, there are ways to compensate for the dispersion of interceptors. Firstly, these are the new fuses in the W76-2 combat warheads, which allow for time-synchronized detonation of the warheads, preventing them from flying past the target. Secondly, there is the mutual overlap of the affected areas when working on a target from several submarines. Thirdly, the U.S. has made progress in hypersonic gliding attack warheads.
A clear sign of the ambition of the United States to deliver such disarming strikes sometime in the future would be evidence that they are firing missiles along flat trajectories, and there is such evidence. Since 2015, three videos of such tests have been filmed by random eyewitnesses—and have become publicly available.
The Americans are clearly working on launching missile strikes using such schemes. And now they are showing us their readiness to bring a strategic submarine to the point of a salvo ‘at point-blank range’. Across Russia.
Of course, it’s easier said than done. One still needs to deploy a sufficient number of submarines to strike. It is necessary not to frighten the enemy and not to cause an emergency exit to the sea of all its strategic missile carriers, not to cause the dispersal of strategic bombers, tankers and cruise missiles with nuclear warheads. What is necessary is that that the mobile ground-based missile systems do not have time to ‘run away’ too far for the inconspicuous B-2 and B—21 bombers, which will go in the second wave to mop up those remnants of the strategic missile forces that would have survived the missile strike—unless the [U.S.] launch team still did not pass through the [Russian] system known as Perimeter [western name, Dead Hand] or otherwise.
It’s all very complicated, and the risks of loss of surprise are very high. But their chances of success are not zero. With the visit of West Virginia to our ‘soft underbelly’, the Americans clearly show how far they are willing to go if they deem it necessary. The Americans are sending an extremely clear signal—for them, nuclear war is no longer unthinkable, and not impossible.