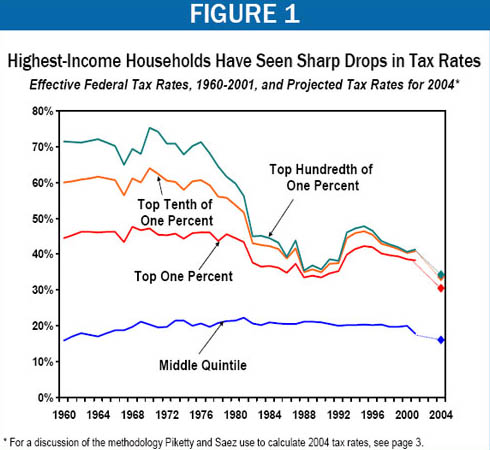
The macro march backward of domestic income and wealth distribution has become remarkable. At least we thought so enough to pen the following remarks. In 2006 the corporate profits share of the national economy retouched its 1929 high. Wage and salary income broke its 8 decade low watermark. Our new economy increasingly replicates the distributional landscape of the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Nowhere is this more clearly demonstrated than in the relation of taxes and income of the richest among us. In their widely published research, Parisian professor Thomas Piketty and his colleague at UC Berkeley, Prof. Emmanuel Saez, have documented how far the progressiveness of the federal income tax has collapsed.1 Using their work, the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities (CBPP) in Washington produced Figure 1 below.2
Notice how sharply the effective tax rates on the highest income earners fell starting in the 1970s. Notice likewise how those tax rates actually rose for the middle fifth of the income distribution in the 1970s, only to fall back again in recent years to about where they were in 1960. Both Democratic and Republican Presidents and Congresses presided over these trends. Debt has kept the realities of our internet-enabled, cutting-edge, early-20th-century economy from being widely understood. The Federal Government borrows back the taxes it fails to collect while spending freely. Toiling multitudes follow suit. They borrow the wages they didn’t get and then some. Thus, consumption booms to 70% of GDP as wages fall as a percentage of our overall economy.
For the top 1 percent of income-earning households in the US, the effective federal income tax rate dropped from around 45% in 1960 to around 30% in 2004, according to the CBPP. At the same time, this top 1% of households saw the portion of total US pre-tax income they received rise from around 9% in 1960 to over 17% in 2004. For the people living in the roughly 1 million households that comprise this top 1 %, the economic news has never been better. The highest shelf cashes in on our cycles of assets appreciation. These are the private investors who performed best during the long stock market booms (1982-2000, 2003-2007) and the real estate booms. Wealth is increasingly top-heavy in distribution and generative of higher income than labor. The rest of the US income distribution sinks deeper into personal debt. Great monies were made loaning ever more to them. As incomes stagnate and liabilities soar, asset bubbles sustain dreams and schemes. We have become a land of Wal-Mart and Net Jets where everyone thinks he is in the middle class. Everyone who is yet to file for our new and improved bankruptcy.
The US economy is still very much caught up in the shifts and adjustments connected to large and sustained changes in distribution of income and tax burden. Trying to hold on to rising standards of living, expected as birthright, households face permanent cash flow crisis as 150 years of rising real wages (decade over decade) ended with the stagnation since the 1970s. How could rising consumption continue without rising wages? Households’ taxes were never significantly reduced, so reduced taxes could not fund consumption. In round one America sent more household members (especially women) out to work. This has morphed into sending all household members to do more labor (shifting from part-time to full-time and taking second jobs). When that proved insufficient, taking on personal debt (home mortgages, home equity lines of credit, 5-year auto loans, credit card debt) exploded. Flat wages, globalization, and financial engineering economically make over and hide deepening lines and failing health. The ride has been spectacular, and may not be over yet.
As debt rises and earnings stagnate, savings go negative. The US had a net negative savings rate over the last year. Where does all the credit come from? Global financial deregulation and rising fragility in financial intermediaries frame the answer. The cheap cash from heavy savings in East Asia and petroleum exporter windfalls finds its way to American consumers. Thus, the IMF reports that, in 2006, the US borrowed 65% of the world’s available savings. We generate about 22% of global GDP and have 5% of the earth’s population. It would seem that our debt and private consumption have moved out of sustainable alignment. This has been partially and temporarily remedied by innovations in debt repackaging and risk sharing. Securitization of debt and derivatives allow for endless repackaging and default risk transfer in rapidly growing speculative and hedging product markets. Thus, the unsustainable becomes routine, profitable, and manageable.
The “collapse of the middle” in the income distribution will likely continue as will the changed burden of taxes. As long as debt levels, delusional understandings, and ready lies from officials oblige. Closed eyes will shield people from reality. Producers, importers, wholesalers, and retailers who miss this process will suffer reverses. Entrepreneurs who see the overall picture evolving will identify the new opportunities. Sadly, the public seems to think that government regulation is their best bet. It would appear they, as well as many liberal commentators, are unaware that the upward redistributions they resent are largely the fruit of government policy shifts.
As the public begins to grasp the precariousness of its position, however, we expect violent attitude re-alignments. The rapid drop in support for globalization and President Bush’s slide from grace will appear slow in comparison to future swings in opinion that we anticipate will be fierce and fast.
1 Thomas Piketty and Emmanuel Saez, “How Progressive Is the U.S. Federal Tax System? A Historical and International Perspective,” Journal of Economic Perspectives, Winter 2007. Thomas Piketty is a professor of economics at the Paris School of Economics. Emmanuel Saez is a professor of economics at the University of California Berkeley. This analysis also relies on data the authors made available on the web:
elsa.berkeley.edu/~saez/jep-results-standalone.xls.
2 Aviva Aron-Dine, writing on website (March 29, 2007) of Center on Budget and Policy Priorities:
www.cbpp.org/3-29-07tax.htm.
 Rick Wolff is Professor of Economics at University of Massachusetts at Amherst. He is the author of many books and articles, including (with Stephen Resnick) Class Theory and History: Capitalism and Communism in the U.S.S.R. (Routledge, 2002) and (with Stephen Resnick) New Departures in Marxian Theory (Routledge, 2006). Max Fraad Wolff is a doctoral candidate in economics at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, and managing director of Global MacroScope. This article was first published in Global MacroScope on 10 April 2007.
Rick Wolff is Professor of Economics at University of Massachusetts at Amherst. He is the author of many books and articles, including (with Stephen Resnick) Class Theory and History: Capitalism and Communism in the U.S.S.R. (Routledge, 2002) and (with Stephen Resnick) New Departures in Marxian Theory (Routledge, 2006). Max Fraad Wolff is a doctoral candidate in economics at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, and managing director of Global MacroScope. This article was first published in Global MacroScope on 10 April 2007.